Overload bit in OSPF and ISIS and behavior on LSPs
Overload bit in IGP is great tool and used for steering traffic away from the node or router whenever there is maintenance need to be done or needs to restart or whatever use case there could be.
In this blog post, I will talk about the overload bit from OSPF and ISIS, I will also talk about the effect of overload bit on transit box on the MPLS LSP.
Lets look at the configuration options available from overload functionality perspective, in both IGPs: ISIS and OSPF.
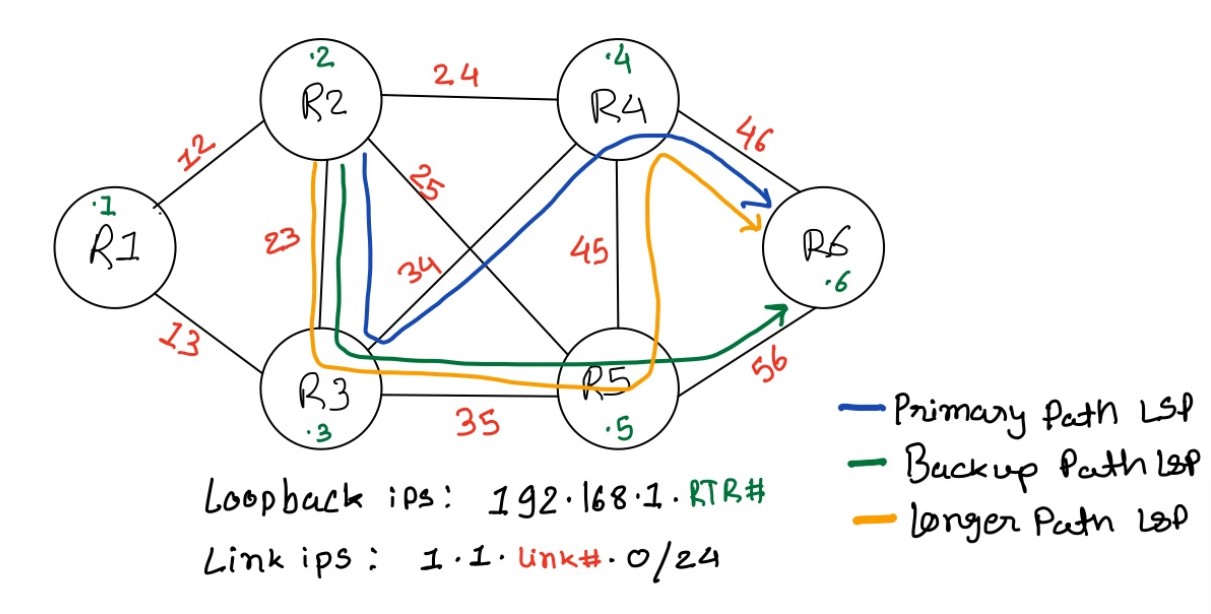
We are going to use this topology:
I have highlighted the important data or fields in the router show output with <<<<<.
For the first test, I have disabled few links in the topology so that the only path to reach R6 from R2 is R2 to R3 to R4 to R5 to R6.
I will start with the ISIS protocol first.
ISIS
Looking at the ISIS configuration stanza or option on JUNOS router:
root@r4# set protocols isis overload ?
Possible completions:
<[Enter]> Execute this command
advertise-high-metrics Advertise high metrics instead of setting the overload bit <<<
allow-route-leaking Allow routes to be leaked when overload is configured
+ apply-groups Groups from which to inherit configuration data
+ apply-groups-except Don't inherit configuration data from these groups
external-prefixes Allow external prefixes to be advertised with high metric
internal-prefixes Allow internal prefixes to be advertised with high metric
timeout Time after which overload bit is reset (60..1800 seconds)
| Pipe through a command
On JUNOS router ISIS configuration options, we see the capability of enabling just overload bit or overload with advertise-high-metrics. Let’s study the difference of both in IP and MPLS LSP perspective.
Baseline show route output on R2 to reach R6’s loopback before enabling the overload bit on R4:
root@r2# run show route 192.168.1.6
Apr 29 09:35:45
inet.0: 28 destinations, 28 routes (28 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
192.168.1.6/32 *[IS-IS/18] 00:00:03, metric 40
> to 1.1.23.2 via ge-0/0/1.23
inet.3: 4 destinations, 5 routes (4 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
192.168.1.6/32 *[RSVP/7/1] 00:00:03, metric 40
> to 1.1.23.2 via ge-0/0/1.23, label-switched-path r2-to-r6
[LDP/9] 00:00:20, metric 1
> to 1.1.23.2 via ge-0/0/1.23, Push 52
When I enabled just overload bit on the router R4 in my topology, R4 will advertise overload bit in the PDU to indicate the node is overloaded.
Lets enable the overload bit on R4 under protocol ISIS configuration:
root@r4# show protocols isis
overload; <<<<<
level 2 wide-metrics-only;
level 1 disable;
interface all {
level 1 disable;
}
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
R2 removed the route to reach R6, only path to reach R6 was via R4 and R4 has announced that it has been overloaded. Here traceroute or ping to R6 loopback would fail since there is no route to reach R6 from R2 perspective.
root@r2# run show route 192.168.1.6
Apr 29 09:34:53
inet.0: 20 destinations, 20 routes (20 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
192.168.0.0/16 *[Static/5] 2w5d 21:09:35
> to 10.49.255.254 via fxp0.0
Let’s look at the ISIS database on R2 to check the status of R4, ISIS R4’s LSP output shows the overload bit set:
root@r2> show isis database extensive r4.00-00
IS-IS level 1 link-state database:
IS-IS level 2 link-state database:
r4.00-00 Sequence: 0x8b7, Checksum: 0x710d, Lifetime: 1181 secs
IS neighbor: r4.02 Metric: 10
Two-way fragment: r4.02-00, Two-way first fragment: r4.02-00
IS neighbor: r4.03 Metric: 10
Two-way fragment: r4.03-00, Two-way first fragment: r4.03-00
IS neighbor: r3.02 Metric: 10
Two-way fragment: r3.02-00, Two-way first fragment: r3.02-00
IS neighbor: r2.02 Metric: 10
Two-way fragment: r2.02-00, Two-way first fragment: r2.02-00
IP prefix: 1.1.24.0/24 Metric: 10 Internal Up
IP prefix: 1.1.34.0/24 Metric: 10 Internal Up
IP prefix: 1.1.45.0/24 Metric: 10 Internal Up
IP prefix: 1.1.46.0/24 Metric: 10 Internal Up
IP prefix: 128.49.229.113/32 Metric: 0 Internal Up
IP prefix: 192.168.1.4/32 Metric: 0 Internal Up
V6 prefix: abcd::128:49:229:113/128 Metric: 0 Internal Up
Header: LSP ID: r4.00-00, Length: 476 bytes
Allocated length: 476 bytes, Router ID: 192.168.1.4
Remaining lifetime: 1181 secs, Level: 2, Interface: 340
Estimated free bytes: 47, Actual free bytes: 0
Aging timer expires in: 1181 secs
Protocols: IP, IPv6
Packet: LSP ID: r4.00-00, Length: 476 bytes, Lifetime : 1196 secs
Checksum: 0x710d, Sequence: 0x8b7, Attributes: 0x7 <L1 L2 Overload> <<<<< OVERLOAD bit set
NLPID: 0x83, Fixed length: 27 bytes, Version: 1, Sysid length: 0 bytes
Packet type: 20, Packet version: 1, Max area: 0
As we dont have route to reach the R6, MPLS LSP from R2 to R6 goes down on R2 as well.
[edit]
root@r2# run show mpls lsp
Apr 29 09:34:58
Ingress LSP: 1 sessions
To From State Rt P ActivePath LSPname
192.168.1.6 192.168.1.2 Dn 0 - r2-to-r6
Total 1 displayed, Up 0, Down 1
Now lets study and observe the behavior of overload bit with advertise-high-metrics configured under ISIS:
root@r4# show protocols isis
overload advertise-high-metrics; <<<<<
level 2 wide-metrics-only;
level 1 disable;
interface all {
level 1 disable;
}
interface fxp0.0 {
disable;
}
On R2’s ISIS database, we can see the metric value of 2^24 which is 16777214.
root@r2> show isis database extensive r4.00-00
IS-IS level 1 link-state database:
IS-IS level 2 link-state database:
r4.00-00 Sequence: 0x8b8, Checksum: 0xa706, Lifetime: 1191 secs
IS neighbor: r4.02 Metric: 16777214 <<<<<
Two-way fragment: r4.02-00, Two-way first fragment: r4.02-00
IS neighbor: r4.03 Metric: 16777214 <<<<<
Two-way fragment: r4.03-00, Two-way first fragment: r4.03-00
IS neighbor: r3.02 Metric: 16777214 <<<<<
Two-way fragment: r3.02-00, Two-way first fragment: r3.02-00
IS neighbor: r2.02 Metric: 16777214 <<<<<
Two-way fragment: r2.02-00, Two-way first fragment: r2.02-00
IP prefix: 1.1.24.0/24 Metric: 10 Internal Up
IP prefix: 1.1.34.0/24 Metric: 10 Internal Up
IP prefix: 1.1.45.0/24 Metric: 10 Internal Up
IP prefix: 1.1.46.0/24 Metric: 10 Internal Up
IP prefix: 128.49.229.113/32 Metric: 0 Internal Up
IP prefix: 192.168.1.4/32 Metric: 0 Internal Up
V6 prefix: abcd::128:49:229:113/128 Metric: 0 Internal Up
Header: LSP ID: r4.00-00, Length: 476 bytes
Allocated length: 476 bytes, Router ID: 192.168.1.4
Remaining lifetime: 1191 secs, Level: 2, Interface: 342
Estimated free bytes: 47, Actual free bytes: 0
Aging timer expires in: 1191 secs
Protocols: IP, IPv6
Packet: LSP ID: r4.00-00, Length: 476 bytes, Lifetime : 1194 secs
Checksum: 0xa706, Sequence: 0x8b8, Attributes: 0x3 <L1 L2>
NLPID: 0x83, Fixed length: 27 bytes, Version: 1, Sysid length: 0 bytes
Packet type: 20, Packet version: 1, Max area: 0
As opposed to disappearing of R6 route on R2, with advertise-high-metrics R6 route is present on R2 but with higher or max metric of 16777244. With MAX metric, route is still a valid route and it will be present in routing and forwarding plane.
root@r2# run show route 192.168.1.6
Apr 29 09:35:31
inet.0: 28 destinations, 28 routes (28 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
192.168.1.6/32 *[IS-IS/18] 00:00:06, metric 16777244 <<<<< route programmed with max metric
> to 1.1.23.2 via ge-0/0/1.23
inet.3: 4 destinations, 4 routes (4 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
192.168.1.6/32 *[LDP/9] 00:00:06, metric 1
> to 1.1.23.2 via ge-0/0/1.23, Push 52
Traceroute or ping to R6 from R2 will be sucessful and showing the path R2 to R3 to R4 to R5 to R6:
root@r2# run traceroute 192.168.1.6
traceroute to 192.168.1.6 (192.168.1.6), 30 hops max, 52 byte packets
1 1.1.23.2 (1.1.23.2) 2.743 ms 2.208 ms 2.609 ms <<<<< R3
2 1.1.34.2 (1.1.34.2) 3.665 ms 3.492 ms 3.669 ms <<<<< R4
3 1.1.45.2 (1.1.45.2) 4.205 ms 4.758 ms 4.210 ms <<<<< R5
4 192.168.1.6 (192.168.1.6) 5.801 ms 5.671 ms 5.621 ms <<<<< R6
With advertise-high-metrics route is still valid, just that it is advertised with the larger metric, LSP will remain up via the R4.
root@r2# run clear mpls lsp optimize all
Apr 29 09:33:51
[edit]
root@r2# run show mpls lsp extensive ingress
Apr 29 09:33:53
Ingress LSP: 1 sessions
192.168.1.6
From: 192.168.1.2, State: Up, ActiveRoute: 0, LSPname: r2-to-r6
ActivePath: (primary)
Node/Link protection desired
LSPtype: Static Configured, Penultimate hop popping
LoadBalance: Random
Follow destination IGP metric
Encoding type: Packet, Switching type: Packet, GPID: IPv4
LSP Self-ping Status : Disabled
*Primary State: Up
Priorities: 7 0
SmartOptimizeTimer: 180
Flap Count: 0
MBB Count: 0
Computed ERO (S [L] denotes strict [loose] hops): (CSPF metric: 16777244)
1.1.23.2 S 1.1.34.2 S 1.1.45.2 S 1.1.56.2 S <<<<< ERO shows R2 to R3 to R4 to R6
Received RRO (ProtectionFlag 1=Available 2=InUse 4=B/W 8=Node 10=SoftPreempt 20=Node-ID):
192.168.1.3(flag=0x20) 1.1.23.2(Label=50) 192.168.1.4(flag=0x20) 1.1.34.2(Label=33) 192.168.1.5(flag=0x20) 1.1.45.2(Label=65) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.56.2(Label=3)
6 Apr 29 09:33:51.113 CSPF: computation result ignored, new path no benefit[2 times]
5 Apr 29 09:32:11.781 Selected as active path
4 Apr 29 09:32:11.780 Up
3 Apr 29 09:32:11.780 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x20) 1.1.23.2(Label=50) 192.168.1.4(flag=0x20) 1.1.34.2(Label=33) 192.168.1.5(flag=0x20) 1.1.45.2(Label=65) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.56.2(Label=3)
2 Apr 29 09:32:11.409 Originate Call
1 Apr 29 09:32:11.409 CSPF: computation result accepted 1.1.23.2 1.1.34.2 1.1.45.2 1.1.56.2
Created: Wed Apr 29 09:32:11 2020
Total 1 displayed, Up 1, Down 0
OSPF
In OSPF there is no concept of overload bit but higher metric is implemented so functionality of it would be same as ISIS advertise-high-metrics scenario. As we can see the OSPF database is populated with max metric of 65535.
root@r4# set protocols ospf overload ?
Possible completions:
<[Enter]> Execute this command
allow-route-leaking Allow routes to be leaked when overload is configured
+ apply-groups Groups from which to inherit configuration data
+ apply-groups-except Don't inherit configuration data from these groups
as-external Advertise As External with maximum usable metric
stub-network Advertise Stub Network with maximum metric
timeout Time after which overload mode is reset (60..1800 seconds)
| Pipe through a command
Let’s look at the OSPF database on R2:
root@r2> show ospf database extensive | match metric | match 65535
Topology count: 0, Default metric: 65535 <<<<< OSPF Max metric
Topology count: 0, Default metric: 65535 <<<<<
Topology count: 0, Default metric: 65535 <<<<<
Topology count: 0, Default metric: 65535 <<<<<
Metric: 65535, Bidirectional
Metric: 65535, Bidirectional
Metric: 65535, Bidirectional
Metric: 65535, Bidirectional
[edit]
root@r4# rollback 1
load complete
[edit]
root@r4# commit
commit complete
[edit]
root@r4# show protocols ospf
[edit]
root@r4#
root@r2> show ospf database extensive | match metric | match 65535
root@r2>
LSP behavior with ISIS with overload bit:
In my topology, I have enabled the redundant links so that LSP can reroute to next available path.
For easy reference, displaying the topology again and enabling the all the links so that we can have redundant paths in topology for LSP to reroute.

In steady state, I have LSP riding from R2 to R3 to R4 to R6 as shown in ERO, the blue path in topology is primary path. Second best path we have is R2 to R3 to R5 to R6, the green path in topology is backup path.
[edit]
root@r2# run show mpls lsp extensive
Apr 29 10:50:42
Ingress LSP: 1 sessions
192.168.1.6
From: 192.168.1.2, State: Up, ActiveRoute: 0, LSPname: r2-to-r6
ActivePath: (primary)
Node/Link protection desired
LSPtype: Static Configured, Penultimate hop popping
LoadBalance: Random
Follow destination IGP metric
Encoding type: Packet, Switching type: Packet, GPID: IPv4
LSP Self-ping Status : Disabled
*Primary State: Up
Priorities: 7 0
SmartOptimizeTimer: 180
Flap Count: 0
MBB Count: 0
Computed ERO (S [L] denotes strict [loose] hops): (CSPF metric: 30)
1.1.23.2 S 1.1.34.2 S 1.1.46.2 S <<<<< ERO shows R2 to R3 to R4 to R6
Received RRO (ProtectionFlag 1=Available 2=InUse 4=B/W 8=Node 10=SoftPreempt 20=Node-ID):
192.168.1.3(flag=0x29) 1.1.23.2(flag=9 Label=57) 192.168.1.4(flag=0x21) 1.1.34.2(flag=1 Label=38) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.46.2(Label=3)
8 Apr 29 10:49:45.970 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x29) 1.1.23.2(flag=9 Label=57) 192.168.1.4(flag=0x21) 1.1.34.2(flag=1 Label=38) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.46.2(Label=3)
7 Apr 29 10:49:45.712 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x21) 1.1.23.2(flag=1 Label=57) 192.168.1.4(flag=0x21) 1.1.34.2(flag=1 Label=38) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.46.2(Label=3)
6 Apr 29 10:49:44.971 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x21) 1.1.23.2(flag=1 Label=57) 192.168.1.4(flag=0x20) 1.1.34.2(Label=38) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.46.2(Label=3)
5 Apr 29 10:49:43.540 Selected as active path
4 Apr 29 10:49:43.538 Up
3 Apr 29 10:49:43.538 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x20) 1.1.23.2(Label=57) 192.168.1.4(flag=0x20) 1.1.34.2(Label=38) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.46.2(Label=3)
2 Apr 29 10:49:43.315 Originate Call
1 Apr 29 10:49:43.315 CSPF: computation result accepted 1.1.23.2 1.1.34.2 1.1.46.2
Created: Wed Apr 29 10:49:43 2020
Total 1 displayed, Up 1, Down 0
Egress LSP: 0 sessions
Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0
Transit LSP: 0 sessions
Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0
Let’s enable only overload bit in ISIS:
[edit]
root@r4# set protocols isis overload
Apr 29 10:50:37
[edit]
root@r4# commit
Apr 29 10:50:50
commit complete
Verify if ISIS database on R2 is reflected with the overload bit:
[edit]
root@r2# run show isis database extensive r4.00-00
Apr 29 10:51:02
IS-IS level 1 link-state database:
IS-IS level 2 link-state database:
r4.00-00 Sequence: 0x8c9, Checksum: 0x4450, Lifetime: 1184 secs
...
Packet: LSP ID: r4.00-00, Length: 397 bytes, Lifetime : 1196 secs
Checksum: 0x4450, Sequence: 0x8c9, Attributes: 0x7 <L1 L2 Overload> <<<<< OVERLOAD bit set
NLPID: 0x83, Fixed length: 27 bytes, Version: 1, Sysid length: 0 bytes
Packet type: 20, Packet version: 1, Max area: 0
In output above we see the overload bit has been propagate, now let’s verify the LSP to check if it’s still via R4 or already moved to path via R5 or do we have to manually trigger optimization.
LSP output on R2 after setting the overload bit on R4:
[edit]
root@r2# run show mpls lsp extensive
Apr 29 10:50:55
Ingress LSP: 1 sessions
192.168.1.6
From: 192.168.1.2, State: Up, ActiveRoute: 0, LSPname: r2-to-r6
ActivePath: (primary)
Node/Link protection desired
LSPtype: Static Configured, Penultimate hop popping
LoadBalance: Random
Follow destination IGP metric
Encoding type: Packet, Switching type: Packet, GPID: IPv4
LSP Self-ping Status : Disabled
*Primary State: Up
Priorities: 7 0
SmartOptimizeTimer: 180
Flap Count: 0
MBB Count: 1
Computed ERO (S [L] denotes strict [loose] hops): (CSPF metric: 30)
1.1.23.2 S 1.1.35.2 S 1.1.56.2 S <<<<< ERO shows R2 to R3 to R5 to R6
Received RRO (ProtectionFlag 1=Available 2=InUse 4=B/W 8=Node 10=SoftPreempt 20=Node-ID):
192.168.1.3(flag=0x29) 1.1.23.2(flag=9 Label=58) 192.168.1.5(flag=0x21) 1.1.35.2(flag=1 Label=74) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.56.2(Label=3)
16 Apr 29 10:50:53.030 Make-before-break: Switched to new instance
15 Apr 29 10:50:52.970 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x29) 1.1.23.2(flag=9 Label=58) 192.168.1.5(flag=0x21) 1.1.35.2(flag=1 Label=74) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.56.2(Label=3)
14 Apr 29 10:50:52.057 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x20) 1.1.23.2(Label=58) 192.168.1.5(flag=0x21) 1.1.35.2(flag=1 Label=74) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.56.2(Label=3)
13 Apr 29 10:50:52.026 Up
12 Apr 29 10:50:52.026 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x20) 1.1.23.2(Label=58) 192.168.1.5(flag=0x20) 1.1.35.2(Label=74) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.56.2(Label=3)
11 Apr 29 10:50:51.703 Originate make-before-break call
10 Apr 29 10:50:51.703 CSPF: computation result accepted 1.1.23.2 1.1.35.2 1.1.56.2
9 Apr 29 10:50:51.702 CSPF: Reroute due to re-optimization
8 Apr 29 10:49:45.970 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x29) 1.1.23.2(flag=9 Label=57) 192.168.1.4(flag=0x21) 1.1.34.2(flag=1 Label=38) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.46.2(Label=3)
7 Apr 29 10:49:45.712 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x21) 1.1.23.2(flag=1 Label=57) 192.168.1.4(flag=0x21) 1.1.34.2(flag=1 Label=38) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.46.2(Label=3)
6 Apr 29 10:49:44.971 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x21) 1.1.23.2(flag=1 Label=57) 192.168.1.4(flag=0x20) 1.1.34.2(Label=38) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.46.2(Label=3)
5 Apr 29 10:49:43.540 Selected as active path
4 Apr 29 10:49:43.538 Up
3 Apr 29 10:49:43.538 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x20) 1.1.23.2(Label=57) 192.168.1.4(flag=0x20) 1.1.34.2(Label=38) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.46.2(Label=3)
2 Apr 29 10:49:43.315 Originate Call
1 Apr 29 10:49:43.315 CSPF: computation result accepted 1.1.23.2 1.1.34.2 1.1.46.2
Created: Wed Apr 29 10:49:43 2020
Total 1 displayed, Up 1, Down 0
Egress LSP: 0 sessions
Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0
Transit LSP: 0 sessions
Total 0 displayed, Up 0, Down 0
In above output we can see in the LSP ERO the r2-to-r6 LSP is rerouted immediately from R4 to R5, there wasn’t any need of manual clear or aggressive-optimize-aggressive.
However in case of overload with advertise-high-metrics in ISIS or overload in OPSF will need the manual optimize-aggressive or need configuration of optimize-aggressive under MPLS on all ingress node.
LSP behavior with advertise-high-metrics:
root@r2# run show mpls lsp extensive
Apr 29 10:52:53
Ingress LSP: 1 sessions
192.168.1.6
From: 192.168.1.2, State: Up, ActiveRoute: 0, LSPname: r2-to-r6
ActivePath: (primary)
Node/Link protection desired
LSPtype: Static Configured, Penultimate hop popping
LoadBalance: Random
Follow destination IGP metric
Encoding type: Packet, Switching type: Packet, GPID: IPv4
LSP Self-ping Status : Disabled
*Primary State: Up
Priorities: 7 0
SmartOptimizeTimer: 180
Flap Count: 2
MBB Count: 0
Computed ERO (S [L] denotes strict [loose] hops): (CSPF metric: 30)
1.1.23.2 S 1.1.34.2 S 1.1.46.2 S <<<<< ERO shows R2 to R3 to R4 to R6
Received RRO (ProtectionFlag 1=Available 2=InUse 4=B/W 8=Node 10=SoftPreempt 20=Node-ID):
192.168.1.3(flag=0x29) 1.1.23.2(flag=9 Label=61) 192.168.1.4(flag=0x21) 1.1.34.2(flag=1 Label=39) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.46.2(Label=3)
25 Apr 29 10:52:52.975 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x29) 1.1.23.2(flag=9 Label=61) 192.168.1.4(flag=0x21) 1.1.34.2(flag=1 Label=39) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.46.2(Label=3)
24 Apr 29 10:52:52.676 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x20) 1.1.23.2(Label=61) 192.168.1.4(flag=0x21) 1.1.34.2(flag=1 Label=39) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.46.2(Label=3)
23 Apr 29 10:52:52.158 Selected as active path
22 Apr 29 10:52:52.157 Up
root@r2# run show isis database extensive r4.00-00
Apr 29 10:53:55
IS-IS level 1 link-state database:
IS-IS level 2 link-state database:
r4.00-00 Sequence: 0x8cb, Checksum: 0x11a6, Lifetime: 1182 secs
IS neighbor: r4.02 Metric: 16777214 <<<<<
Two-way fragment: r4.02-00, Two-way first fragment: r4.02-00
IS neighbor: r4.03 Metric: 16777214 <<<<<
Two-way fragment: r4.03-00, Two-way first fragment: r4.03-00
IS neighbor: r3.02 Metric: 16777214 <<<<<
Two-way fragment: r3.02-00, Two-way first fragment: r3.02-00
IP prefix: 1.1.24.0/24 Metric: 10 Internal Up
IP prefix: 1.1.34.0/24 Metric: 10 Internal Up
IP prefix: 1.1.45.0/24 Metric: 10 Internal Up
IP prefix: 1.1.46.0/24 Metric: 10 Internal Up
IP prefix: 128.49.229.113/32 Metric: 0 Internal Up
IP prefix: 192.168.1.4/32 Metric: 0 Internal Up
V6 prefix: abcd::128:49:229:113/128 Metric: 0 Internal Up
Header: LSP ID: r4.00-00, Length: 397 bytes
Allocated length: 476 bytes, Router ID: 192.168.1.4
Remaining lifetime: 1182 secs, Level: 2, Interface: 338
Estimated free bytes: 47, Actual free bytes: 79
Aging timer expires in: 1182 secs
Protocols: IP, IPv6
Packet: LSP ID: r4.00-00, Length: 397 bytes, Lifetime : 1196 secs
Checksum: 0x11a6, Sequence: 0x8cb, Attributes: 0x3 <L1 L2>
NLPID: 0x83, Fixed length: 27 bytes, Version: 1, Sysid length: 0 bytes
Packet type: 20, Packet version: 1, Max area: 0
root@r2# run show mpls lsp extensive
Apr 29 10:53:58
Ingress LSP: 1 sessions
192.168.1.6
From: 192.168.1.2, State: Up, ActiveRoute: 0, LSPname: r2-to-r6
ActivePath: (primary)
...
Computed ERO (S [L] denotes strict [loose] hops): (CSPF metric: 30)
1.1.23.2 S 1.1.34.2 S 1.1.46.2 S <<<<< ERO shows R2 to R3 to R4 to R6
Received RRO (ProtectionFlag 1=Available 2=InUse 4=B/W 8=Node 10=SoftPreempt 20=Node-ID):
192.168.1.3(flag=0x29) 1.1.23.2(flag=9 Label=61) 192.168.1.4(flag=0x21) 1.1.34.2(flag=1 Label=39) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.46.2(Label=3)
25 Apr 29 10:52:52.975 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x29) 1.1.23.2(flag=9 Label=61) 192.168.1.4(flag=0x21) 1.1.34.2(flag=1 Label=39) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.46.2(Label=3)
As we can see above in MPLS LSP ERO, even after the database is updated with the higher metric, LSP is still riding on the old path via R4. We need to optimize manually using optimize-aggressive.
root@r2# run clear mpls lsp optimize-aggressive all
Apr 29 10:54:17
After manual optimization, we can see the LSP is transiting via R5.
[edit]
root@r2# run show mpls lsp extensive
Apr 29 10:54:20
Ingress LSP: 1 sessions
192.168.1.6
From: 192.168.1.2, State: Up, ActiveRoute: 0, LSPname: r2-to-r6
ActivePath: (primary)
Node/Link protection desired
LSPtype: Static Configured, Penultimate hop popping
LoadBalance: Random
Follow destination IGP metric
Encoding type: Packet, Switching type: Packet, GPID: IPv4
LSP Self-ping Status : Disabled
*Primary State: Up
Priorities: 7 0
SmartOptimizeTimer: 180
Flap Count: 2
MBB Count: 1
Computed ERO (S [L] denotes strict [loose] hops): (CSPF metric: 30)
1.1.23.2 S 1.1.35.2 S 1.1.56.2 S <<<<< ERO shows R2 to R3 to R5 to R6
Received RRO (ProtectionFlag 1=Available 2=InUse 4=B/W 8=Node 10=SoftPreempt 20=Node-ID):
192.168.1.3(flag=0x29) 1.1.23.2(flag=9 Label=62) 192.168.1.5(flag=0x21) 1.1.35.2(flag=1 Label=77) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.56.2(Label=3)
33 Apr 29 10:54:19.179 Make-before-break: Switched to new instance
32 Apr 29 10:54:19.023 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x29) 1.1.23.2(flag=9 Label=62) 192.168.1.5(flag=0x21) 1.1.35.2(flag=1 Label=77) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.56.2(Label=3)
31 Apr 29 10:54:18.970 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x29) 1.1.23.2(flag=9 Label=62) 192.168.1.5(flag=0x20) 1.1.35.2(Label=77) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.56.2(Label=3)
30 Apr 29 10:54:18.175 Up
29 Apr 29 10:54:18.174 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x20) 1.1.23.2(Label=62) 192.168.1.5(flag=0x20) 1.1.35.2(Label=77) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.56.2(Label=3)
28 Apr 29 10:54:17.901 Originate make-before-break call
27 Apr 29 10:54:17.901 CSPF: computation result accepted 1.1.23.2 1.1.35.2 1.1.56.2
26 Apr 29 10:54:17.900 CSPF: Reroute due to re-optimization
25 Apr 29 10:52:52.975 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x29) 1.1.23.2(flag=9 Label=61) 192.168.1.4(flag=0x21) 1.1.34.2(flag=1 Label=39) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.46.2(Label=3)
24 Apr 29 10:52:52.676 Record Route: 192.168.1.3(flag=0x20) 1.1.23.2(Label=61) 192.168.1.4(flag=0x21) 1.1.34.2(flag=1 Label=39) 192.168.1.6(flag=0x20) 1.1.46.2(Label=3)
23 Apr 29 10:52:52.158 Selected as active path
22 Apr 29 10:52:52.157 Up
optimize-aggressive configuration example:
root@r2# set protocols mpls optimize-aggress?
Apr 29 11:55:48
Possible completions:
optimize-aggressive Run aggressive optimization algorithm based on IGP metric only
In summary:
- with only overload bit in ISIS, route will go away and LSP will optimize right away or will go down if no alternate path available.
- Overload bit in OSPF is same as overload bit with
advertise-high-metricswhere links are advertise with 16777214 in ISIS and 65535 in OSPF. Since both the metric is still a valid metric, routes via overloaded nodes will be reflected with higher metric and LSPs will need manual optimization on headend to move them away from the overloaded node.
